Recently, I got involved with a requirement to build a Salesforce CRM roadmap for a client. Here is the context of this requirement
- The client will be implementing Salesforce for the first time
- The client needs a lot of education about Salesforce CRM and the Force.com platform
- The client has multiple needs for Salesforce
- Client needs to be educated on how they can leverage the Force.com platform to built Enterprise apps integrated with CRM and which can be a conduit between CRM and the existing ERP application landscape
Our prescription is to build a Roadmap is to use the TOGAF V9.1 Architecture development methodology. Due to the paucity of time, the client only wants to focus mainly on capability and implementation roadmap.
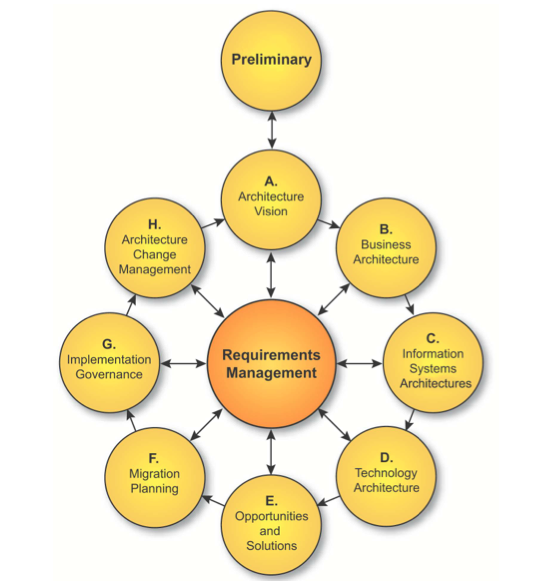
To build the Roadmap, we will be focusing mainly on the Business Architecture component of this methodology with some emphasis on the implementation methodology. Other, components will be included only 10-20% as they involve separate effort.
Let’s quickly see what can be done with each one of these components and then I will describe how we can get to a roadmap.
Architectural Vision
- Definition of Stakeholders and Business Goals
- Corporate Goals influencing CRM Vision
Business Architecture and Strategy
We will use this component specifically to build the roadmap. Here are the questions we can attempt to answer by Business Architecture and Strategy
- What lines of Business will use Salesforce?
- Business requirements definition
- Identification of Key Business challenges
- Key Performance indicators
- Analysis of Current Vs Desired CRM State
- What business processes will be implemented on and influenced by SFDC (Process and Capability Mapping)
- Definition of High-Level Salesforce Org Strategy
- Salesforce License Options
- Identification of Applications in the Salesforce Ecosystem E.G à Vlocity
- Definition of High-level Business requirements
- Salesforce Roadmap by Capability and Processes
Information systems Architecture
- Application Architecture and Rationalization Plan
- Data Architecture
- Gap-Fit Analysis
Technology Architecture
- Integration Architecture
- Custom development architecture
- Management of Technical Environments and Risk mitigation
Solution and Implementation Methodology
- Cognizant’s Hybrid Implementation Methodology
- Release Strategy
- Implementation Roadmap
Migration Planning
- Deployment Strategy
- Test Strategy
- Data Conversion Planning
Governance Planning
- Architecture Review Board
- System Admin Model for Salesforce
- App and Vendor Management
- Establishment of Salesforce & CRM COE
- Integration of Efforts
Change Management Planning
- How to management change with CRM Transformations
- Salesforce Org change Management
- Training strategy
Now, Let’s see what we can do to get to the Roadmap. We will be mainly using the Business Architecture and Strategy component of the above framework to get to the Roadmap.
This is the exact sequence of steps we will go through to get to the Roadmap:
Step 1 – Definition of Stakeholders and Business Goals – This will involve the identification of parties interested in the CRM Program Management and Implementation. This could be program and project sponsors, various business unit leaders, etc. Business goals must be identified for e.g. One call customer complaint resolution, quoting efficiency, reduced quote time, building a unified view of the customer, historical bill analysis. These are either already defined by the business or requires a series of steps to set. Here are some steps through which business goals can be determined
Step 2 – Discovery and Current state analysis – Current systems, processes, scenarios, pain points must be discovered and analyzed. For example, the current CRM system has to be studied and analyzed, current processes implemented in the CRM system have to be understood and studied, CRM integrations with enterprise applications have to study, a list has to be prepared for processes that are carried out manually. This can be done through the following actions
- System walkthrough’s
- Interview of the process leaders
- Study of existing documentation
- Study of repeatable tickets
- Interaction with the supervisors
- Creation of current process/persona flows
Step 3 – Gap analysis, Future state analysis, Process, and Capability Mapping to Salesforce CRM – After studying the current application and processes, pain points with the current process must be identified, future goals and objectives must be set and capabilities must be identified, For example, the current call center and the front end processes are not operating optimally, the customer are not getting a unified multichannel experience, quota and territory management is done on paper and excel, there is no way to assign opportunities by territory, sales pipelines are not managed on paper, many key business reports are created in excel with inconsistent data, leads are not qualified and many leads are not processed, quotes are often inaccurate and the turnaround time on a quote is high. So, as a result, the following objectives and capabilities get identified
Objective 1- One call customer complaint resolution – Capability – Customer Service
Objective 2- Customer experience should consistent across the enterprise-Capability -> Omnichannel and a 360-degree view of the customer
Objective 3- Opportunities should be assigned by Territory and quotas should be managed systematically – Capability – Territory Management
Objective 4- Sales Pipelines should be accurate and be reported on a regular basis – Capability- Pipeline Management
Objective 5- Actionable and insightful reports to be created from the system which should be shared with the appropriate users and be systemically created and scheduled – Capability – Reporting
Step 4– In addition to the capability and objective definition, specific scenarios should also be identified. For example, if let’s say the client is an energy/utility company, they will have industry-specific processes like Move in- Move Out, Shift of services, Reporting of Hazardous Incident, Bill Analysis, New Opt in’s, etc. These scenarios can either be handled by a generic CRM application like Salesforce or need a specialized application Vlocity which is built on Salesforce CRM.
Finally, a list of capabilities, objectives, and scenarios, can be mapped to the single or multiple CRM applications. These objectives can be prioritized and can take shape of a capability-based Roadmap along with the mapped applications. This answers the question of the roadmap based on capability. The next step is to derive an implementation roadmap which should be MVP (Minimum Viable Product) based. This could be a combination of multiple or a single capability, but it needs to be a wave and MVP based phased rollout.
I hope this gave you all a flavor of how using an enterprise structure methodology, we can create a Roadmap for CRM Implementation. Your likes, comments, and shares will keep me motivated.

1 Comment
porno
November 13, 2020 - 2:39 pmMajor thankies for the blog article. Much obliged. Angeline Haydon Pettit